Benefits of using PoE Power Management Controllers in Power Sourcing Equipment
Power over Ethernet (PoE) Basics
It is important to understand some fundamental aspects of Power over Ethernet IEEE 802.3af (PoE up to 15.4W) 802.3at (PoE+ up to 30W) and 802.3bt (Hi-PoE up to 100W).
Ethernet cables (CAT 5e and better) contain four twisted pair wires. In 10 and 100BASE-TX Ethernet, only two of these pairs are used to deliver data. Gigabit Ethernet (1000Base-T) requires the use all four pairs.
Given that two conductors are required to deliver power over a cable, the PoE standard treats each pair as a single conductor. It can use the two data pairs (referred to as Phantom Power or Alternative A) or the two spare pairs (Alternative B) to carry the electrical current. Because Gigabit requires 4 data pairs, PoE in Gigabit links will transmit power over two of the data pairs (Phantom Power).
Power is injected onto the Ethernet cable at a voltage between 44 and 57 volts DC (50 to 57 volts for PoE+ and Hi-PoE). This allows efficient power transfer along the cable, while still meeting the low voltage requirements of the SELV (Safety Extra Low Voltage) standard.
Safety Extra Low Voltage Standard
The SELV standard specifies the process required for the safe application of power on a network cable. The Signature Detection, Classification, Start-up, Operation and Disconnect stages are explained.
Signature Detection
Even though 44 and 57 volts DC is safe for users, it can damage equipment that has not been designed to receive PoE power. Therefore, as part of the IEEE standard, before Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) can enable power to a connected Powered Device (PD) – like and IP camera or wireless access point -- it must perform a qualification check to ensure that the Ethernet device can receive power. This is done through a signature detection process.
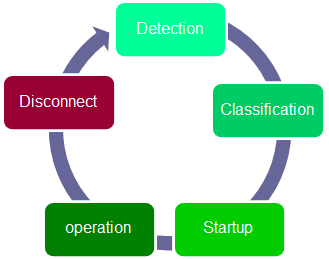
Signature detection is performed by injecting a very small voltage on the link to detect a characteristic signature of IEEE-compatible PDs. This is presented with a 25k ohm resistance. Once detected, the PSE knows that higher voltages can be safely applied. A device not supporting this standard will not present this signature and voltage will not be applied. This means that on a remote switch with multiple PoE PSE ports, the connection of various types of Ethernet equipment can be safely done with compliant and non-compliant PoE PDs. It is important to note that Passive PoE injectors do not perform this check and will always apply power on the cable. These devices have visual warnings on the ports to not connect non-PoE complaint devices, however, that does not guarantee that staff at remote sites will not inadvertently connect a device to the wrong port.
Classification
Classification follows the signature detection stage and determines the amount of power for which a device is rated. If a PD displays a classification signature, it lets the PSE know how much power it requires to operate. This means that PSEs with a limited total power budget can allocate it effectively. PoE power classes and types are as follows:
| IEEE PoE Specifications for Cat5e @100m | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard / Type | 802.3af Type 1 |
802.3at Type 2 |
802.3bt Type 3 |
802.3bt Type 4 |
||||
| Name / Year | PoE / 2003 | PoE+ / 2009 | Hi-PoE / 2018 | Hi-PoE / 2018 | ||||
| PSE Input Voltage (Min) | 44V/50V | 50V | 52V | |||||
| Supported PD Class | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| PSE Output Power to Single-Signature PD | 4W | 6.7W | 14W | 30W | 45W | 60W | 75W | 90W - 100W |
| Single-Signature PD Input Power (Min) | 3.84W | 6.49W | 13W | 25.5W | 40W | 51W | 62W | 71.3W |
| PSE Output Power to Dual-Signature PD (per pairset) | 4W | 6.7W | 14W | 30W | 45W | -- | -- | -- |
| Dual-Signature PD Input Power (pairset / total) | 3.84W / 7.68W |
6.49W / 12.98W |
13W / 26W |
25.5W / 51W |
35.6W / 71.2W |
-- | -- | -- |
| Ethernet Pairs | 2-Pair | 2-Pair or 4-Pair |
4-Pair | |||||
The table above represents the power available at the PSE. It is important to note that because of cable resistance, voltage drops along the length of the cable occur and power is lost resulting in less power being available to the remote PD. As an example, a PSE detecting a Class 3 device will provide up to 15.4 watts. However on a full 100 meter cable, no more than 12.95 watts will be available to the remote PD.
If a PD does not display a classification signature, a class 0 level of power is used.
Start-up
Following the detection and classification of a newly connected device, voltage is applied in a controlled manner so that unwanted noise is not injected into the cable eventually reaching the full negotiated PoE power level required.
Operation Monitoring
Once full voltage is applied the PSE continues to monitor how much electrical current it is being delivered to the PD and will cut the power to the cable if too much, or not enough, power is drawn. This protects the PSE and PD against overload and ensures that PoE is disconnected from the cable if the PD is unplugged.
Disconnect
If, during the operation, the cable is disconnected the PSE will remove the voltage from the cable within 15 to 20ms. This ensures that voltage is removed in the event that a non-PoE compliant device is then connected.
Smart PoE Management Controller
Properly designed PoE PSEs will have PoE Management Controllers built into the product which meet the IEEE 802.3af/at/bt standards. This ensures that:
- both PoE and non-PoE complaint devices can be safely connected;
- unwanted noise is not injected on the network cable during power up;
- current draw is constantly being monitored for protection of both the PSE and PD;
- voltage is removed immediately upon disconnect enabling a non-PoE device to be connected if desired.
Identifying a non-compliant PSE is easily determined through the visual warnings displayed on the product‘s PoE port(s) or user guide.
Perle PoE PSE's with built-in Power Management Controllers
Perle PoE Ethernet Extenders are the only VDSL- based Ethernet Extenders on the market that have a built-in PSE controller that is fully compliant with PoE standards. Competitive PoE Ethernet Extender products operate as a simple passive power injector and will always apply power to RJ45 port pins which may result in damage if non-PoE compliant Ethernet devices are accidently attached.



