LTE Routers and Gateways: Everything you need to know
By Julie McDanielVice President Marketing
August 12, 2024
In this digital age, seamless and reliable internet connectivity is everything. The evolution of networking devices like routers and gateways transforms how we connect with the world. Today, we're casting the spotlight on LTE and 5G-enabled routers and gateways, exploring their potential and why they might be the ideal solution for your connectivity needs.
An Introduction to Routers and Gateways
In the simplest of terms, a router is a device that forwards data packets on computer networks. It operates at the heart of the network layer of a LAN or WAN. The data packets consist of multiple layers, each containing different information. Of these layers, one is responsible for identifying the sender, data type, size, and, most importantly, the destination IP (Internet Protocol) address. The router reads this layer, prioritizes the data, and uses its dynamically updated routing table to decide the most suitable path for transmitting the data. Think of a router as your digital postman, delivering appropriate data to different devices in your network swiftly and efficiently.
In contrast to a router, a gateway acts as the 'gate' through which data enters or exits a network. A gateway not only sends and receives data but also translates it if necessary. For instance, it can connect networks that use different protocols and handle data conversion and translation so that the data transmitted from one network can be interpreted and used in a different network. A gateway is also commonly referred to as an edge router or modem.
While they may seem similar, routers and gateways play different roles in networking. While routers primarily connect devices within the same network and aid in directing internal and external communication, gateways enable data to flow seamlessly between different networks, often handling protocol translation along the way. Traditional routers and gateways rely on wired connections, typically Ethernet cables, for the best signal quality and data transmission rates.
Defining LTE & 5G Cellular Routers and Gateways
LTE routers offer benefits to the traditional connectivity in other routers. These cellular routers, also called wireless routers, have a built-in modem to connect to a defined broadband mobile data network-like 4G LTE or 5G-to offer users wireless wide-area network (WWAN) access. The same is true for cellular gateways.
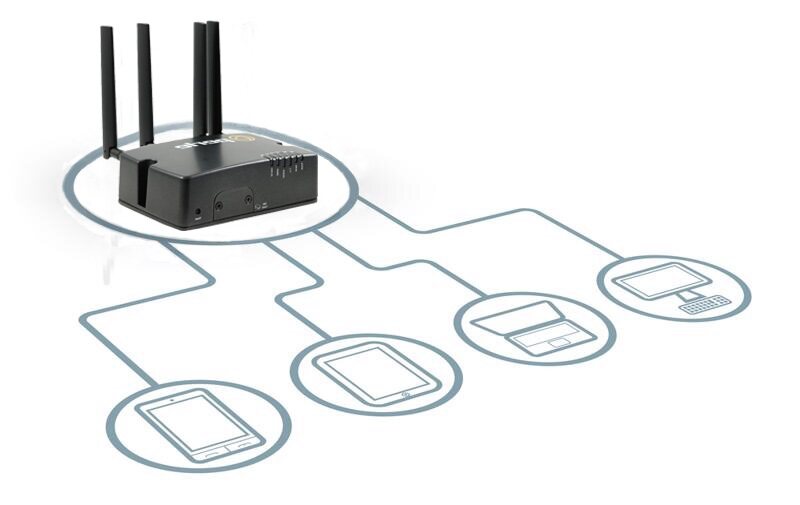
This connection is established through the activation of a SIM card. An integral part of any cellular router, the SIM card enables the router to connect to the network of a specific telecommunications service provider, facilitating the transmission of data over the LTE or 5G cellular network. Because cellular routers and gateways connect to the internet wirelessly by utilizing the same technology and networks that mobile phones use, they offer excellent portability and flexibility. By removing the need for physical infrastructure, routers and gateways with integrated LTE or 5G capabilities are optimal for locations where wired internet access is not available or automatic failover is desirable.
Understanding the difference between Enterprise LTE Routers and Home LTE Routers
Wireless networks have become incredibly popular and convenient, leading to a surge in demand for LTE and 5G routers in the mainstream market. However, users need to understand the differences between enterprise and home routers before making a purchase decision. This understanding can help them make an informed choice and get a router that best suits their needs.
- Performance & Speed: Enterprise routers have a Central Processing Unit (CPU) that provides superior stability and faster performance. They also contain flash memory that will save unsent data during power outages or device restarts. This powerful feature, unavailable in-home routers, ensures no data is lost. Home routers also typically have less RAM than enterprise routers, resulting in slower speeds due to limited data throughput and forwarding frequency.
- Security & Network Integration: Home routers, designed for simple network environments, are not equipped with enterprise-grade security protocols, which makes them more vulnerable to hackers and attacks. Furthermore, enterprise routers come with more advanced routing protocols, enhanced security, and unified management protocols, which ensure their safe integration into hierarchical or large mesh network structures. Complexities found in enterprise networks require powerful routers to meet the requirement for additional WAN interfaces, higher bandwidth, load balancing, flow control, VPNs, and secure communications.
- Ruggedized Reliability: When it comes to M2M and IoT applications, such as video surveillance systems, digital signage, telehealth services, and more, only enterprise routers can pass the critical certification testing required for safe and reliable use. These high-end routers are designed with top-of-the-line components, making them ideal for use in rugged outdoor environments, mass transit, and even smart city infrastructure. Their ruggedized hardware can withstand hazardous industrial environments with high levels of electrical energy, explosive gases, extreme temperatures, dust, water splash, or vibration. Plus, a select few of these enterprise-grade routers are designed to operate in ultra-low power environments, such as those powered by batteries, solar, or wind. Home routers will not suffice.
- Quality & Price: One of the main differences between home routers and enterprise routers is the cost. Due to their enhanced design and functionality, enterprise routers are much more expensive, typically $500 to $2,000, while a regular home router costs only between $20 and $50. However, enterprise routers are designed to last for over a decade. In contrast, home routers are usually replaced after one to two years when users upgrade to a newer product.
Why LTE VPN Routers Are a Powerhouse for Secure Enterprise Networks
In our modern era, where data breaches are commonplace, securing your data has never been more critical. LTE VPN routers unite VPN (Virtual Private Network) support with the speed and reliability of LTE or 5G to provide a high-speed, private internet connection in enterprise networks. By integrating these two technologies, LTE VPN routers protect your data by creating a secure, end-to-end encrypted communication tunnel for your sensitive data. Sectors like healthcare, finance, legal, IT services, and others with stringent data security requirements can significantly benefit from such advanced levels of secure connectivity.
Choosing the Right Cellular Router or Gateway for Your Needs
Choosing an LTE or 5G wireless router balances cost, connection speed, coverage area, technical specifications, and compatibility with your existing network and security infrastructure. Your varied needs, depending on the size of your business or goals, will ultimately determine which tool is best suited for you.
As we move deeper into the 21st century, technology continues to evolve at an unparalleled pace. LTE routers and gateways will become more efficient, cost-effective, and user-friendly. Faster and more secure connections will revolutionize industries heavily dependent on strong and steady internet connectivity. From healthcare to logistics, the spectrum of industries that could see a marked improvement in their operations and services is vast and exciting.
In conclusion, cellular routers and gateways represent a powerful chapter in the evolution of networking devices, offering more comprehensive coverage, higher data transmission rates, and an unprecedented level of reliable connectivity. As we lean more into the digital age, embracing and effectively utilizing these networking tools will open doors of opportunities and advancements. Knowing and understanding the key differences in the technology tools available to you and your business can better prepare you for the ever-evolving digital world.



